LIFE EXPECTANCY Life expectancy (or the expectation of life) is the average length of life remaining to be lived by a population at a given age It is computed in the process of building a life table and can be computed for any age in the life table Life expectancy at birth is the most commonly presented value because this measure provides a succinct indicator of mortality that This life expectancy can be attributed to better healthcare services including immunisation drives across the countries and adequate medical staff Mauritius In Mauritius, the life expectancy is 744, making it the third African country on the list Not only does the country have one of the lowest fertility rates but also the lowest infant mortality ratesGain in life expectancy over the years For instance, in Rwanda the life expectancy has risen from a low of 267 years between 1992 – 1993 to 690 years in 19 The remarkable improvement in life expectancy recorded in Rwanda can be linked to, among other factors, the reforms and health initiatives being implemented by the government
2
Low life expectancy in africa can be partly attributed to the ravages of aids
Low life expectancy in africa can be partly attributed to the ravages of aids-There has been much less progress in South Africa (due mainly to the epidemic of HIV/AIDS) and the Russian Federation (due mainly to the impact of the economic transition in the 1990s and the rise in risky behaviours among men) In the last couple of years, a number of OECD countries reported slight falls in life expectancy Following four decades of gains, life expectancy in South Africa has fallen dramatically—from 61 years in the early 1990s to 51 years today In Zimbabwe, where 10 percent of the population are infected with HIV, the change has been even more dramatic life expectancy fell from 62 to 43 years between 1985 and 05



2
Part of the answer lies in what is called the Bangladesh Paradox The country has developed a pluralistic health system that has stakeholders pursuing women centered, genderequityoriented, highly focused health programs in family planning , alon In Africa, however, the life expectancy at birth is only 52 years Although it can be partly attributed to a widespread HIV/AIDS epidemic in Africa, low socioeconomic status is a major contributor It is obvious that rapid population growth in subSaharan Africa is driven by high fertility rate and poor family planningIncreasing life expectancy to welfare for countries from 1870, offers an analysis with a nearglobal scope from 1950, and covers the adverse implications of a negative health shock (HIV/AIDS) Various measures of life expectancy are explored, and the implications of different methods of discounting are discussed
Based on the life expectancy value, Nigeria is ranked 216 in the world, and 16th in Africa However, this LE value and the country's ranking is expected to increase over the next few years By , the average life expectancy in Nigeria will rise to 5523 years ranking the country 214 globally and 14th in Africa Life expectancy is one of the methods used to measure health in various countries Countries with low life expectancy at birth is most likely to have problems with health care and the number of years that is expected to live, while countries with high life expectancy at birth tends to have minor problems with health care and longevity This simply summarizes that the level of Introduction The surge in life expectancy in the African region since 00 is evidently the greatest since the reverse gains in the 1990s Life expectancy at birth increased in the region by 94 years to 60 years, with some countries experiencing as high as 42% rise between 00 and 14 These remarkable gains have taken place mainly in the context of increased
This sharp incline in life expectancy of lowincome countries is attributed to a greater access to aid programs and organizations than ever before A Stanford study found that countries receiving the most health aid gained five or more years in average life expectancy The leading causes of death in subSaharan Africa for adults 15 to 49 years were AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, maternal disorders, andObesity might lower life expectancy rates African American women have a life expectancy of 747 years Experts predict that life expectancy rates in developed nations may lower because of obesity The average American male lives for 736 years, but a nutritious diet and exercise can go a long way toward raising that average




The Embodiment Of Inequality Aids As A Social Condition And The Historical Experience In South Africa Embo Reports Vol 4 No S1




How Covid 19 Is Affecting The Global Response To Aids Tuberculosis And Malaria Friends Of The Global Fight
Life expectancy in Africa plummets due to Aids Aids has devastated many areas of Africa Life expectancy is likely to virtually halve in Zimbabwe because of Aids, according to a US report The US Census Bureau report, to be published next month, shows that average life expectancy in Zimbabwe is expected to fall from 61 to 39 by the year 10 The second reason for the changes in life expectancy in Africa could be attributed to the rapid decline in the child mortality rate The percentage of infant and child deaths (out of 1,000 live births) fell between 1970 and 13 — from 138 to just 67 in every 1,000 births In subSaharan Africa, Aids is now the leading cause of death and is considered to have cut life expectancy in some countries by as much



Purl Access Gpo Gov
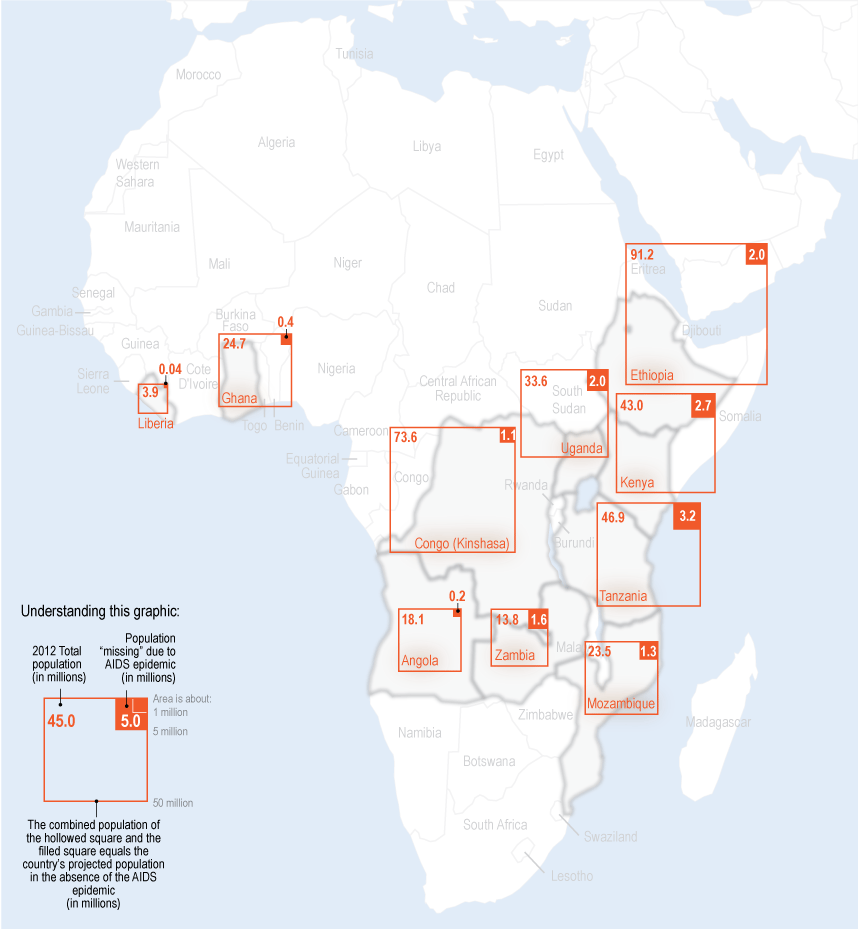



Hiv Aids Impact In Africa
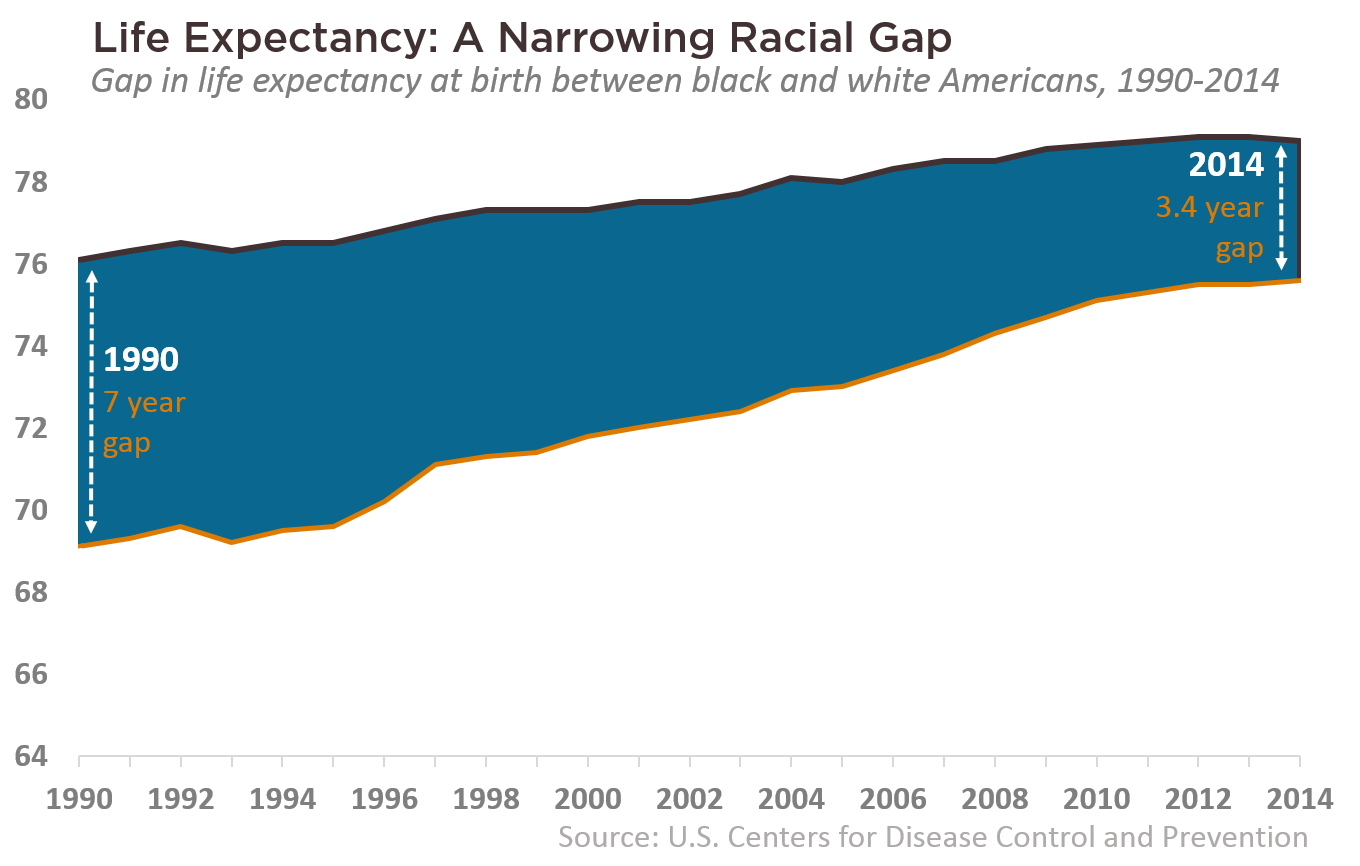
Between 00 and 09, life expectancy at birth increased more for African Americans than for Whites, narrowing the life expectancy gap between these two racial groups, the report shows In 00, life expectancy at birth for Whites was 55 years longer than for the Blacks By 09, though, the difference narrowed to 43 years219th South Africa – Although it has the largest economy in Africa, and the 28th largest in the world, estimates for this country explicitly take into account the aftereffects of apartheid excess mortality due to AIDS, resulting in very low life expectancy of 4941 years, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, and lower population growth ratesLife expectancy is low This may be due to lack of clean drinking water, proximity to the hospital or health care center, etc Some less developed countries, life expectancy at birth may be lower than life expectancy at age 1, because of high infant mortality rates commonly due to lack of access to a clean water supply or infectious disease To




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect
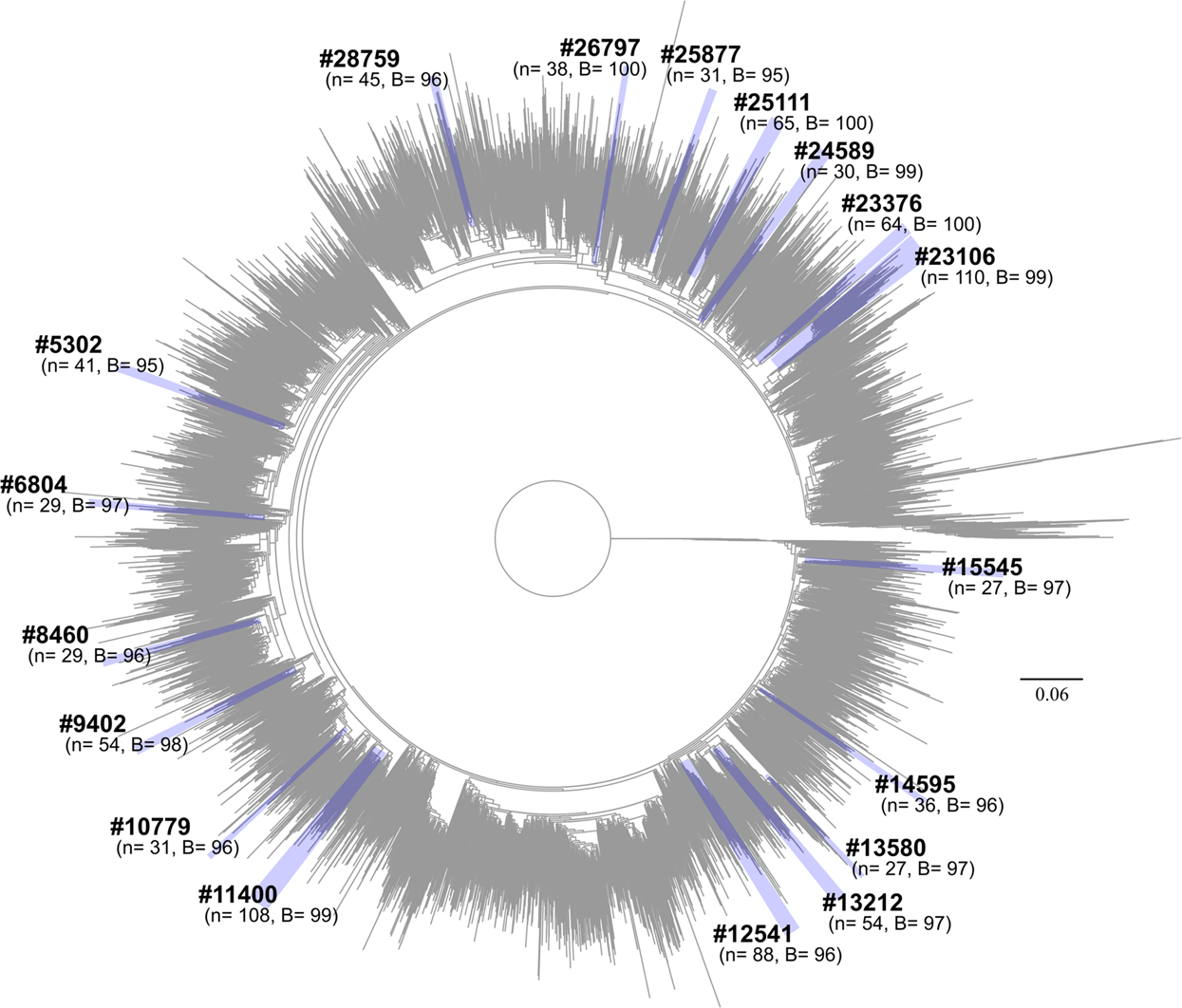



The Effect Of Interventions On The Transmission And Spread Of Hiv In South Africa A Phylodynamic Analysis Scientific Reports
The World Health Organisations World Health Statistics 18 report shows that two of the biggest reasons for the decreased life expectancy in South Africa are TB and HIV South Africa has the biggest HIV epidemic in the world with 71 million people living with HIV and the HIV prevalence in the general population being a high 1% Health and welfare improvements are one of the main reasons why life expectancy in Africa has been on the rise One of the biggest health issues that Africa has been plagued with is the HIV/AIDS epidemic HIV/AIDS has tragically claimed many lives in Africa, which is a large reason why life expectancy was so lowA High Standard of Living, Brought Low by AIDS in South Africa In 1994 South Africa's regime of apartheid, under which the black majority was suppressed and discriminated against by the white minority, came to an end 1 The African National Congress (ANC) won the first free elections in the same year, and the paty has held power ever since



Assets Publishing Service Gov Uk




Approved The Economist
Kenya even regressed before moving upward again Kenyans' life expectancy is slightly above the African average (565 years) but it has lost ground since the late 1980s (then 60 years and not far from the global average) It declined in the 90s to 51 years, mainly due to HIV/AIDS, before recovering over the last decadeThe worst life expectancies are found in Africa with its lower economic development and very high rate of mortality from HIV/AIDS infection The top ten populations in terms of descending life expectancy (52 to 8059 years) are Andorra, Macao, Japan, Singapore, San Marino, Hong Kong, Sweden, Australia, Switzerland, and France According to the WHO (World Health Organisation), South Africa's average life expectancy is 636 years, based on 16 data Here's how we compare to some other countries While these figures only show an average, South Africa's life expectancy is fairly low compared to other countries If you don't already have it, taking out whole life



2




Africans Are Living Longer Than At Any Point In The Last 25 Years Quartz Africa
"The increase in life expectancy can be attributed to the constant improvement in the implementation of comprehensive strategies to combat the quadruple burden of diseases inclusive of communicable disease, primarily HIV and AIDS and Tuberculosis, and the reduction in infant and child mortality rates," said Minister Radebe While the report shows a global spike in life expectancy across the various regions, Africa has gained the most increase with life expectancy up The blackwhite gap in life expectancy in the United States is currently about 36 years, which is a 50% reduction from 1970 1,2This promising national trend




The Perfect Storm Incarceration And The High Risk Environment Perpetuating Transmission Of Hiv Hepatitis C Virus And Tuberculosis In Eastern Europe And Central Asia The Lancet



2
Africa's Underdevelopment An Issue of External Influence Iwok, U M and low life expectancy among others This review opined that all the hydra multinationals and resistance to military aids and assistance among others can go a long way in repositioning Africa's pride The countries with the lowest life expectancy worldwide include the Central African Republic, Chad, and Lesotho As of 19, people born in the Central African Republic could be expected to liveRates decreased in these countries by 675%, 654%, 636%, and 618% respectively Causes of Death One of the major causes of underfive mortality is neonatal sepsis In 10, 15% of newborn deaths in Africa can be attributed to infections related to the delivery process




Hiv Aids Impact In Africa




Public Health And Population Health Understanding Health And Disease Springer Publishing
One of the poorest countries in the world, the Central African Republic had the second lowest level of human development, ranking 187th out of 1 countries in 14 As the country´s population has been permanently devastated by a variety of diseases and healthrelated problems including measles, malaria, HIV/AIDS, female genital mutilation etc, it currently has the A low life expectancy is a strong indication of economic underdevelopment Nigeria's low life expectancy also raises some concerns over an official retirement age of 625 years (the average for male and female) A life expectancy below the official retirement age underscores the extent of loss to the country's productive work force Human development in subSaharan Africa has stagnated while progress in other parts of the world has accelerated, widening the gap between the world's richest and poorest countries, warns this year's United Nations Human Development Index (HDI), which finds life expectancy in the region lower today than 30 years ago mainly because of the ravages of



Cgdev Org




The Cancer Miracle Isn T A Cure It S Prevention Harvard Public Health Magazine Harvard T H Chan School Of Public Health
The life expectancy jumped from 509 years in 12, to 538 years in 15, according to the report Deaths resulting from the 10 biggest health risks in Africa – such as lower respiratory infections, HIV and diarrhoeal diseases – dropped by half between 00 and 15, partly as a result of specialised health programmes The five leading causes of death in subSaharan Africa for adults between the ages of 15 and 49 years in 17 were AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, maternal disorders, and road injuries Lack of food & malnutrition seems to be one of the major factors contributing to low life expectancy (2) Governments too poor to spend Many of the African countries are said to be poor There are just so many of them which are classified as HIPC (Highly Indebted Poor Countries) where they owe huge sum of money to IMF & World Bank




Approved The Economist



Ustr Gov
Life expectancy at birth was on average 806 years across OECD countries in 15 ( Figure 31 ) There have been substantial gains in life expectancy over time, with life expectancy at birth on average ten years higher today than it was in 1970 A number of countries reported slight falls in life expectancy between 14 and 15, though The rise in life expectancy can be attributed to two important trends first, the number of AIDS related deaths is estimated to have decreased from 363 910 deaths in 05 (51% of all deaths) to 171 733 deaths in 14 (31% of all deaths) This can be associated with the increased rollout of antiretroviral therapy (ART)Table 2 Life Expectancy Gaps GNP in 1999 US$ PPP Life Expectancy at Birth Gap to Highest life expectancy in the low income group Gap to highest life expectancy in Africa Gap to highest life expectancy globally Zaire 384 5 64 130 90 Sierra Leone 414 398 186 130 90 Tanzania 478 509 75 130 90 Burundi 553 495 130 90




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan




How Covid 19 Is Affecting The Global Response To Aids Tuberculosis And Malaria Friends Of The Global Fight
Life expectancy at birth increased 15 years be In Africa, a high mortality of HIV/Aids tancy at birth of the world can be attributed to the decreas The average life expectancy across the whole continent was 61 years for males and 65 years for females The average life expectancy However, it then decreased by nine years between 1990 and 10, and has since dropped to 5161 years This contrasts with the global trend towards increased life expectancy HIV/Aids is still prevalent in South Africa 348 per cent of all deaths in the country can be attributed to HIV/Aids and tuberculosis



2
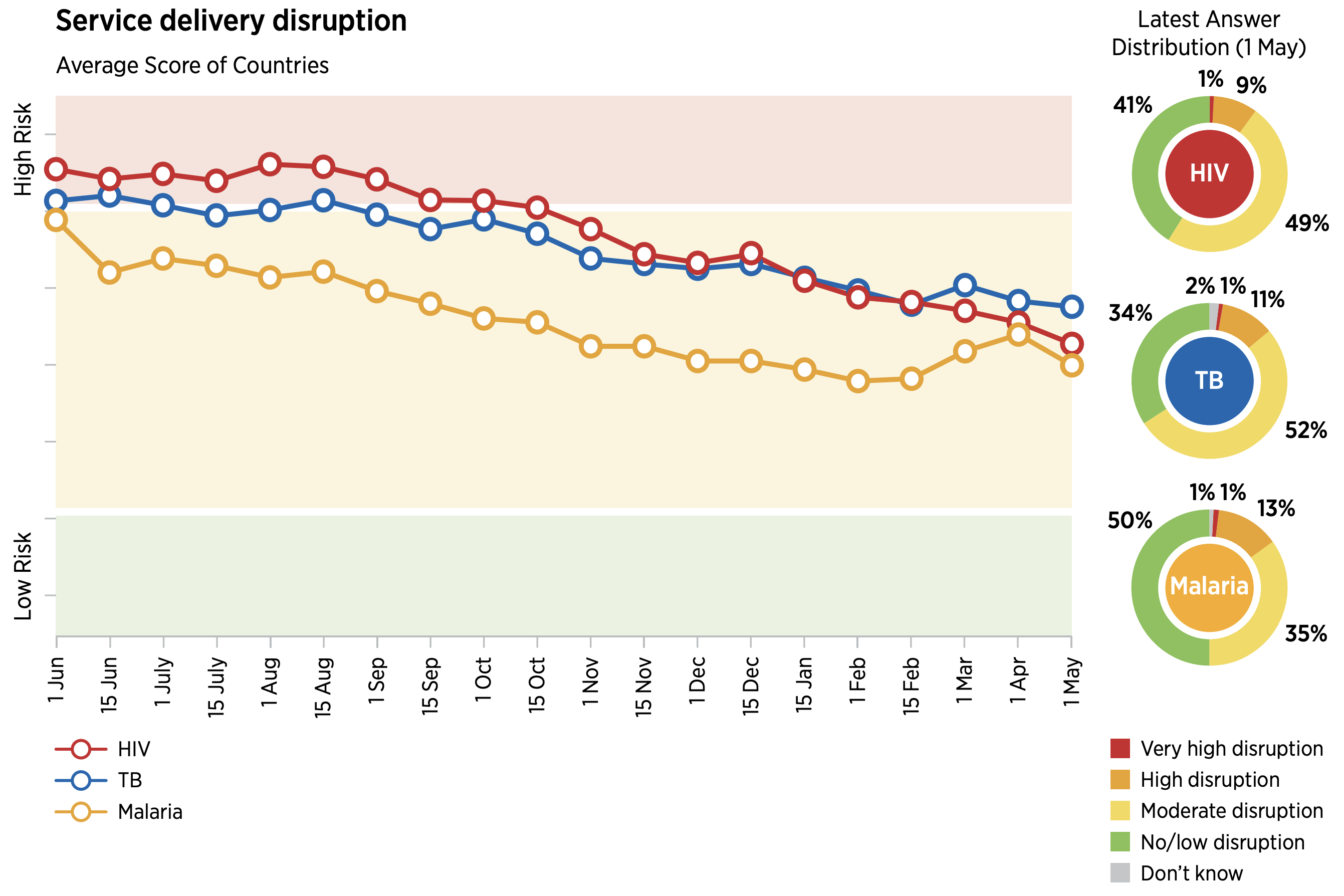



How Covid 19 Is Affecting The Global Response To Aids Tuberculosis And Malaria Friends Of The Global Fight




How Covid 19 Is Affecting The Global Response To Aids Tuberculosis And Malaria Friends Of The Global Fight



2



2




Adult Mortality In The Cities Of Bulawayo And Harare Zimbabwe 1979 08 Dlodlo 11 Journal Of The International Aids Society Wiley Online Library
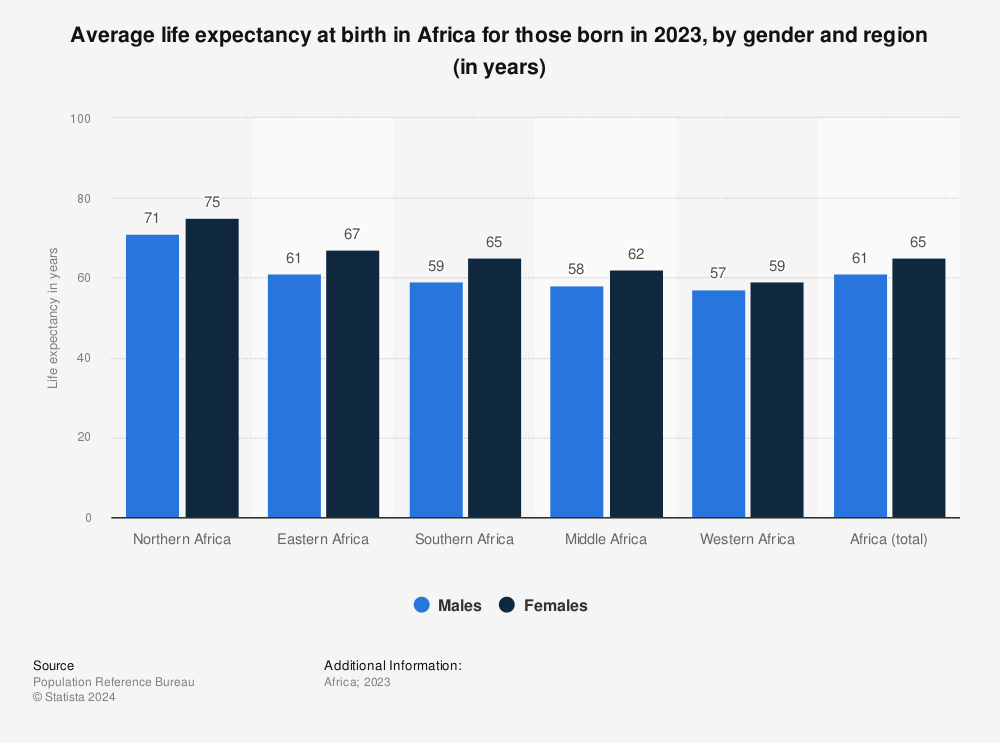



Life Expectancy In Africa 19 Statista



Data Highlights 21 Troubling Health Trends Holding Back Progress On Life Expectancy Epi
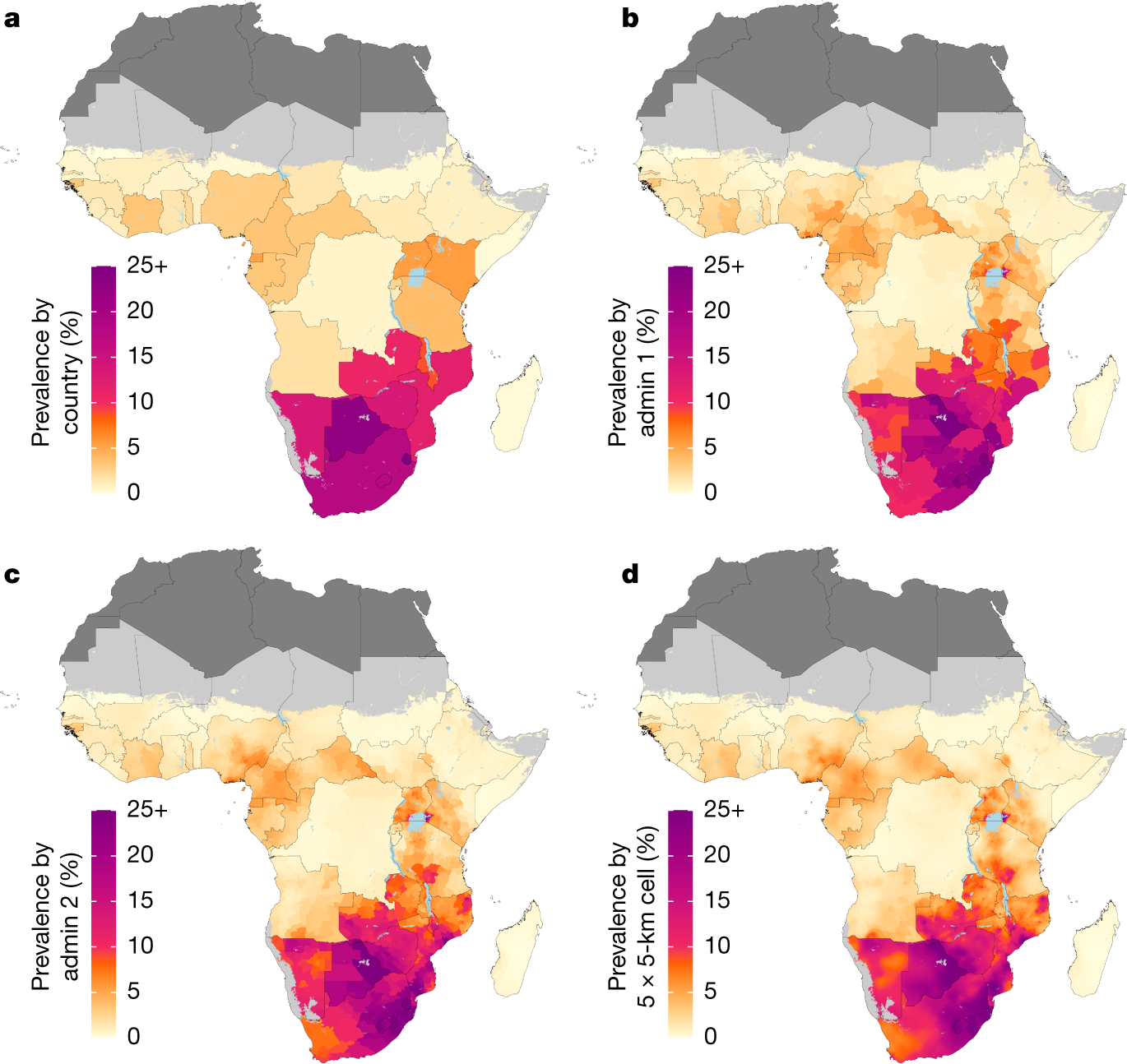



Mapping Hiv Prevalence In Sub Saharan Africa Between 00 And 17 Nature




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect




Coronavirus Pandemic The Interpreter




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan




Africa Life Expectancy 1950 Statista



2




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan




Black Americans See Gains In Life Expectancy The New York Times



Scholarworks Umt Edu




A Century Of Hiv Origins Current Events In Historical Perspective




South Africa Life Expectancy 1870 Statista



2



2




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect
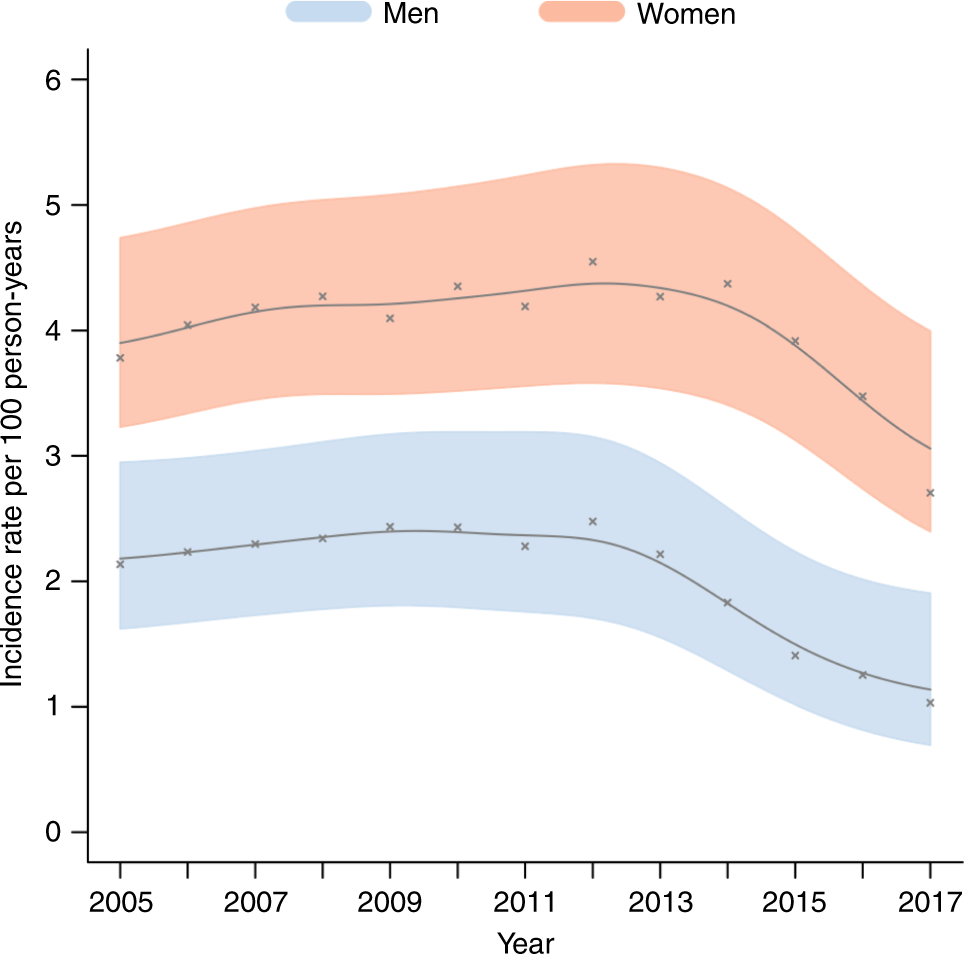



Declines In Hiv Incidence Among Men And Women In A South African Population Based Cohort Nature Communications




Tackling The Challenges To Health Equity In China The Lancet




Public Health And Population Health Understanding Health And Disease Springer Publishing
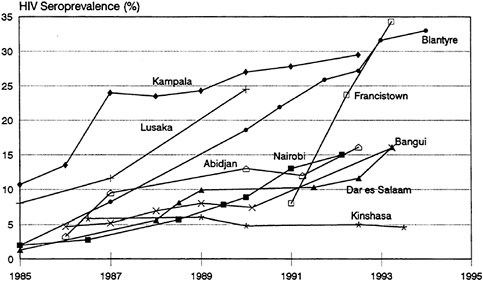



3 Epidemiology Of The Hiv Aids Epidemic Preventing And Mitigating Aids In Sub Saharan Africa Research And Data Priorities For The Social And Behavioral Sciences The National Academies Press




Approved The Economist




Why Is The Number Of Covid 19 Cases Lower Than Expected In Sub Saharan Africa A Cross Sectional Analysis Of The Role Of Demographic And Geographic Factors Sciencedirect
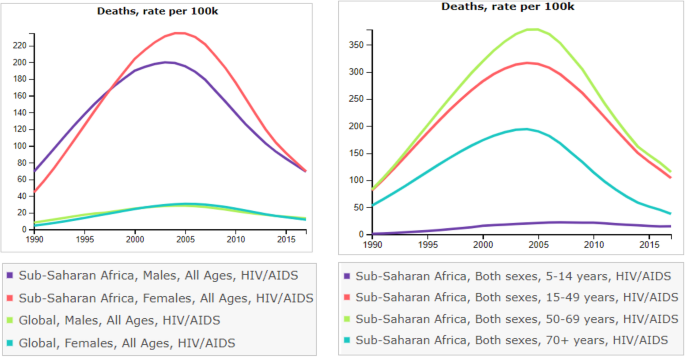



Burden And Changes In Hiv Aids Morbidity And Mortality In Southern Africa Development Community Countries 1990 17 Bmc Public Health Full Text




The Embodiment Of Inequality Aids As A Social Condition And The Historical Experience In South Africa Embo Reports Vol 4 No S1




Adult Mortality In The Cities Of Bulawayo And Harare Zimbabwe 1979 08 Dlodlo 11 Journal Of The International Aids Society Wiley Online Library




Black Americans Have Fewer Years To Live Here S Why Data Mine Us News




Health Care Reform And The Crisis Of Hiv And Aids In South Africa Nejm




Feminist Art Coalition



Life Expectancies Of South African Adults Starting Antiretroviral Treatment Collaborative Analysis Of Cohort Studies




Approved The Economist



2



2




References In Global Burden Of Disease In Young People Aged 10 24 Years A Systematic Analysis The Lancet



2




Russia S Demographic Crisis Rand



2



Black White Life Expectancy Gap Cut In Half Since 1990 Bread For The World




Human Geography People Place And Culture 9th Edition Fouberg Test Bank



2




Approved The Economist




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect



Clintonwhitehouse5 Archives Gov




Public Health And Population Health Understanding Health And Disease Springer Publishing




Lancet Covid 19 Commission Statement On The Occasion Of The 75th Session Of The Un General Assembly The Lancet




North Carolina Literary Review Online By East Carolina University Issuu




Africa Life Expectancy 1950 Statista



2




South Africa Life Expectancy 1870 Statista



Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly




The Embodiment Of Inequality Aids As A Social Condition And The Historical Experience In South Africa Embo Reports Vol 4 No S1




Hiv Aids In Africa



Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan




Infographic Life Expectancy In South Africa From 1960 To 15 South Africa Gateway




Estimating Trends In Life Expectancy In Hiv Positive Individuals The Lancet Global Health



2




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect




The Cancer Miracle Isn T A Cure It S Prevention Harvard Public Health Magazine Harvard T H Chan School Of Public Health



Global Risks 35 The Search For A New Normal Atlantic Council




How Covid 19 Is Affecting The Global Response To Aids Tuberculosis And Malaria Friends Of The Global Fight




The Embodiment Of Inequality Aids As A Social Condition And The Historical Experience In South Africa Embo Reports Vol 4 No S1



2




Scielo Brasil Hiv Aids In South Africa An Overview Hiv Aids In South Africa An Overview



2




Life Expectancy In Africa



2



Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly



The Human Rights Of People Living With Hiv Aids In China Hrw



2



2




Hiv Aids Is No Longer The Leading Cause Of Death In Africa World Economic Forum




Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus And Obesity In Sub Saharan Africa Tuei 10 Diabetes Metabolism Research And Reviews Wiley Online Library



2



2
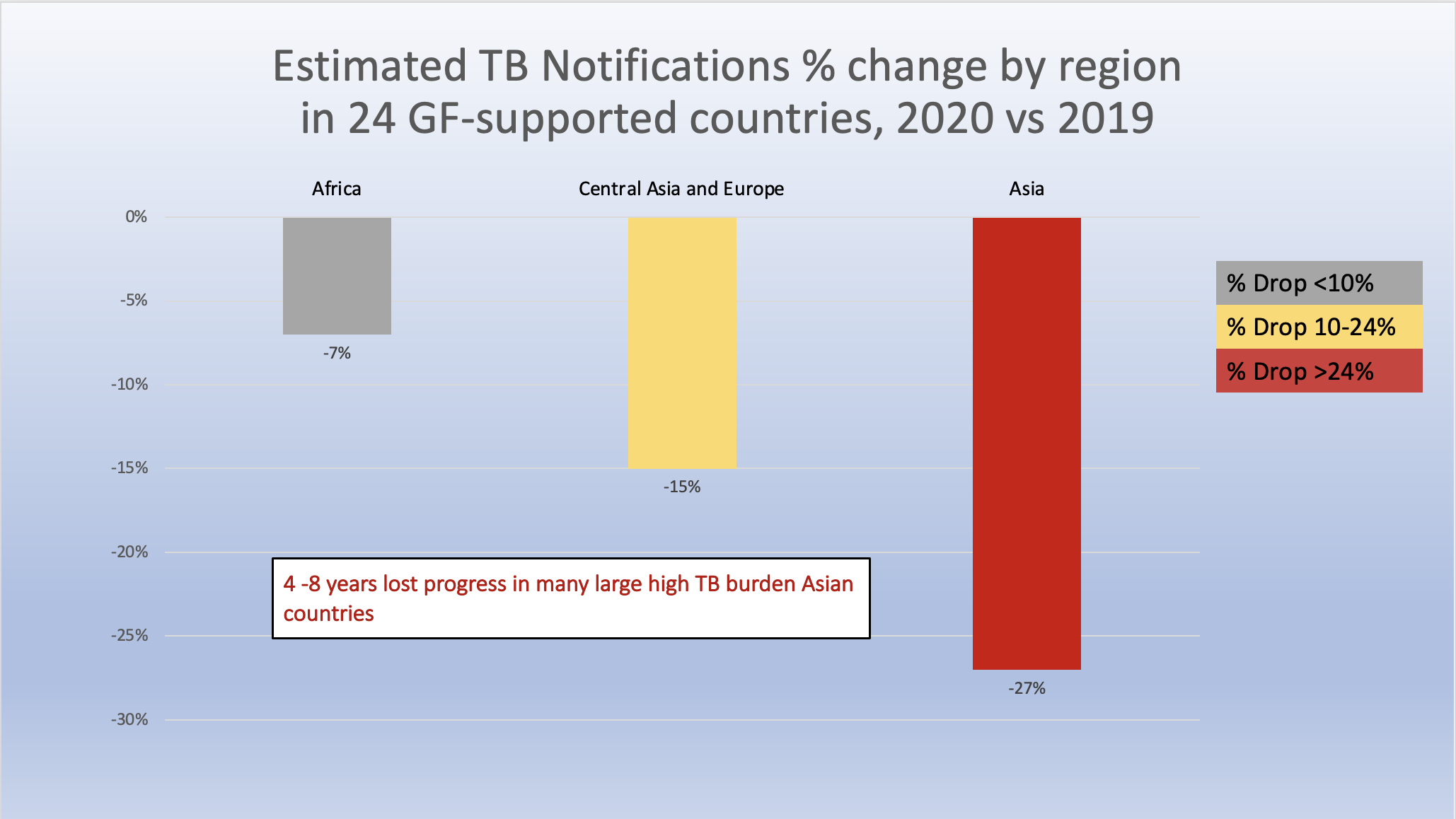



How Covid 19 Is Affecting The Global Response To Aids Tuberculosis And Malaria Friends Of The Global Fight



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿